In Java, a method is like a function which is used to expose the behavior of an object.
Method in Java is a collection of instructions
that performs a specific task. It provides the reusability of code. The
most important method in Java is the main() method.
1.
Types of Method
There are two types of methods in Java:
- Predefined Method
- User-defined Method
Predefined
Method
In Java, predefined methods are the method that is
already defined in the Java class libraries. It is also known as the standard
library method or built-in method.
These methods can be used just by calling them in
the program at any point. When a call is made to any of the predefined methods
in our program, a series of codes related to the corresponding method runs in
the background that is already stored in the library.
Some pre-defined methods are length(),
equals(), compareTo(), sqrt(), etc.
Example:
System.out.print("The maximum number is: " + Math.max(9,7));
in above example the print() method is a method
of PrintStream class that prints the result on the console.
The max() method is a method of the Math class that returns
the greater of two numbers.
User-defined
Method
The method written by the user or programmer
according to the requirement is known as a user-defined method.
User defined methods have to be declared and called
to perform a task.
1.
Method Declaration
The method declaration provides information about
method attributes, such as visibility, return-type, name, and arguments.
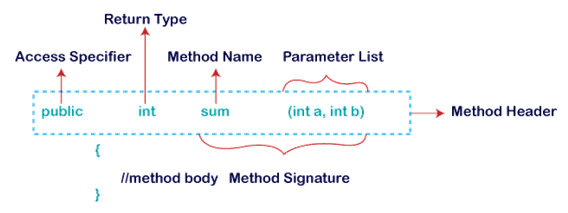
Access
Specifier: Access specifier or modifier is the access
type of the method. It specifies the visibility of the method. Java
provides four types of access specifier:
- Public: The method is accessible by all classes when we use public
specifier in our application.
- Private: If a private access specifier is used, the method is
accessible only in the classes in which it is defined.
- Protected: If a protected access specifier is used, the method is
accessible within the same package or subclasses in a different package.
- Default: When no access specifier is used in the method declaration,
Java uses default access specifier by default. It is visible only from the
same package only.
Return
Type: Return type is a data type that the method
returns. It may have a primitive data type, object, collection, void, etc. If
the method does not return anything, void keyword is used.
Method
Signature: Every method has a method signature. It is a
part of the method declaration. It includes the method name and parameter
list.
Method
Name: It is a unique name that is used to define the
name of a method. It must be corresponding to the functionality of the method.
A method is invoked by its name.
Parameter
List: It is the list of parameters separated by a
comma and enclosed in the pair of parentheses. It contains the data type and
variable name. If the method has no parameter, left the parentheses blank.
Method
Body: It is a part of the method declaration. It
contains all the actions to be performed. It is enclosed within the pair of
curly braces.
2.
Method Call:
Once a method have been defined, it should be called
(invoked) to perform the operation of the method. When a user defined method is
called or invoked, the program control is transferred to the called method. A
method can also be called multiple times.
Example:
public class Demo {
static void
myMethod() // method declaration
{
System.out.println("I just got executed!");
}
myMethod(); // method call
}
}
No comments:
Post a Comment